In an era where data breaches, fraud, and lack of transparency dominate headlines, blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking solution. Initially known as the core technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved into a powerful tool with far-reaching applications across industries. Its ability to provide secure, decentralized, and tamper-proof records makes it a cornerstone of the digital future.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that allows data to be recorded across multiple computers so that the records cannot be altered retroactively without the consensus of the network. Each record, called a block, is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks—hence the name blockchain.
Key Characteristics:
-
Decentralized: No single authority controls the data.
-
Immutable: Once recorded, data cannot be changed.
-
Transparent: All transactions are visible to participants.
-
Secure: Advanced cryptography protects the data.
How Does Blockchain Work?
-
Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction (e.g., sending digital currency or recording data).
-
Block Creation: The transaction is grouped with others into a block.
-
Validation: Participants (nodes or miners) validate the block using consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
-
Adding to the Chain: Once validated, the block is added to the chain in chronological order.
-
Completion: The transaction is complete, and the ledger is updated across all nodes.
Types of Blockchain
-
Public Blockchain: Open to everyone (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
-
Private Blockchain: Restricted to specific participants (e.g., enterprise use).
-
Consortium Blockchain: Controlled by a group of organizations.
-
Hybrid Blockchain: Combines features of public and private chains.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
1. Finance and Banking
-
Instant cross-border payments
-
Fraud detection and reduction
-
Smart contracts for automated compliance
2. Supply Chain Management
- Real-time product tracking
-
Eliminating counterfeit goods
-
Transparent vendor audits
3. Healthcar 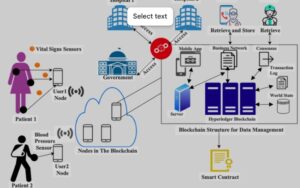
-
Secure patient data sharing
-
Medical record integrity
-
Drug traceability
4. Voting Systems
-
Tamper-proof electronic voting
-
Voter identity verification
-
Transparent results auditing
5. Real Estate
-
Smart contracts for property sales
-
Land record management
-
Fraud prevention
6. Intellectual Property
-
Proof of ownership for creators
-
Automated royalty payments
-
Preventing piracy
Benefits of Blockchain
-
✅ Enhanced Security: Cryptographic algorithms protect data from hacks.
-
✅ Greater Transparency: Everyone on the network has access to the same data.
-
✅ Improved Efficiency: Automation reduces manual intervention and errors.
-
✅ Reduced Costs: Cuts out intermediaries and transaction fees.
-
✅ Traceability: Every transaction is recorded and auditable.
Challenges and Limitations
-
⚠️ Scalability: Processing large volumes of transactions is still slow.
-
⚠️ Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms are power-intensive.
-
⚠️ Regulatory Uncertainty: Global legal frameworks are still developing.
-
⚠️ Complexity: Requires technical expertise to implement and manage.
-
⚠️ Data Privacy: In public blockchains, ensuring personal data privacy can be difficult.
The Future of Blockchain
The future of blockchain is bright and transformative:
-
Web 3.0: A decentralized internet where users own their data.
-
CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies): Governments exploring blockchain for national currencies.
-
Tokenization of Assets: Real estate, stocks, and art represented as digital tokens.
-
Interoperability: Different blockchains working seamlessly together.
-
AI and IoT Integration: Smarter, automated, and secure machine-to-machine communication.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is not just a buzzword; it is a revolutionary advancement poised to redefine trust, security, and transparency in digital systems. As industries increasingly adopt blockchain solutions, its role in creating a safer, more transparent world becomes ever more vital. Whether it’s in finance, healthcare, supply chains, or governance, the potential of blockchain to drive innovation and efficiency is limitless.
Embracing blockchain today means building a more secure and trustworthy tomorrow